PEPPER
NCT00961181
First-In-Human Trial - Paclitaxel-Releasing Balloon in Patients Presenting with In-Stent Restenosis
Conclusion
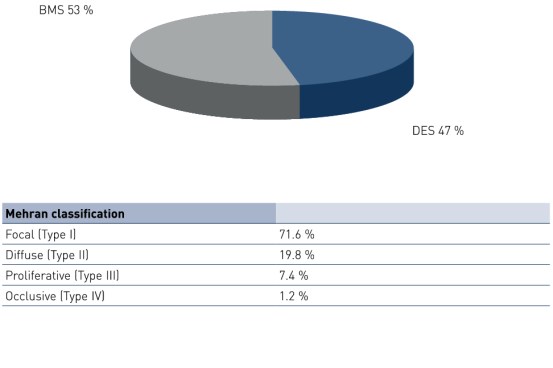
- Application of a paclitaxel-coated balloon using butyryl-tri-hexyl citrate (BTHC) as an excipient is feasible and safe in a mixed population of patients with predominantly type I bare metal stent (BMS) or drug-eluting stent (DES) in-stent restenosis (ISR) lesion.
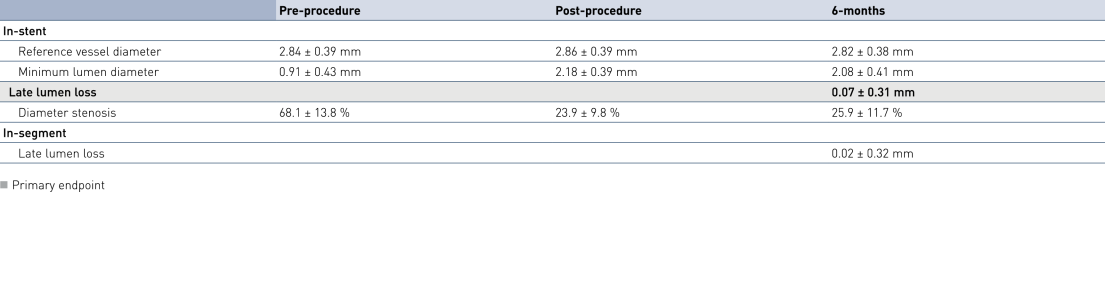
- A short exposure of the vessel wall to paclitaxel results in very low late lumen loss, revascularization and major adverse cardiac events (MACE) rates.
- Pantera Lux application is a valuable treatment option for ISR in both BMS and DES patients.
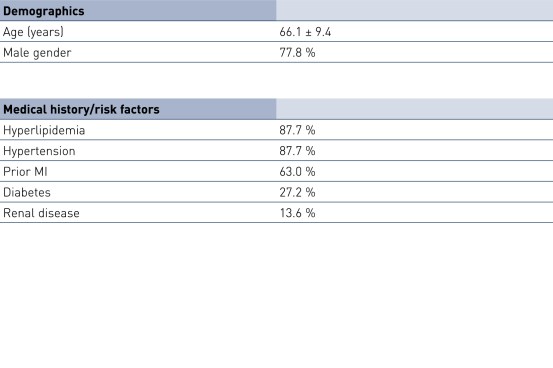
Baseline Characteristics and ISR Distribution by Stent Type
Image
Image
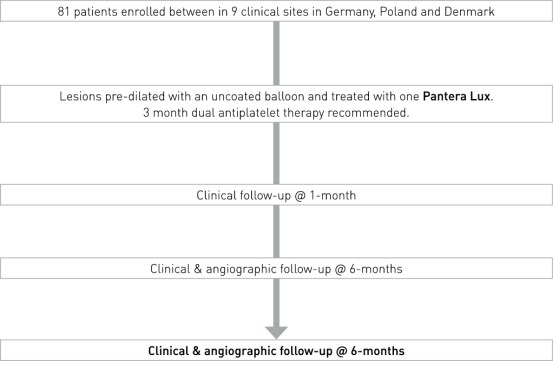
Study Design
- Prospective, multi-center, non-randomized European clinical trial
- Number of patients (n): 81
- Principal Investigator: Dr. Chistoph Hehrlein, University Medical Center Freiburg, Germany
- Primary endpoint: In-stent late lumen loss (LLL) at 6 months
- Clinical sites: 9 sites in Germany, Poland and Denmark
Image
Acute and 6-months Angiographic Results
Image
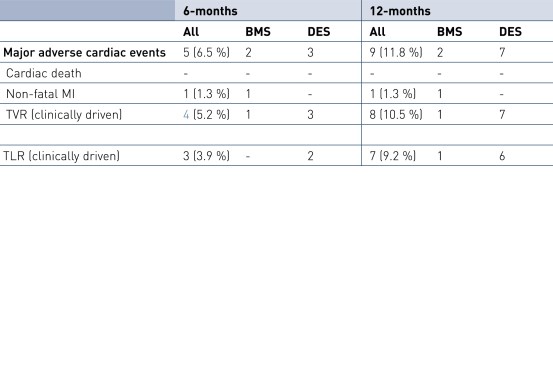
6 and 12-Month Clinical Results
Image
Downloads
Vascular Intervention
Paclitaxel-Releasing BalloonClinically proven solution in both in-stent restenotic and de novo lesions

Vascular Intervention
Clinical StudyDrug-Releasing Pantera Lux PTCA Balloon Catheter Registry
Source:
Hehrlein C et al. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2012; 13(5): 260-4.
© BIOTRONIK AG
All rights reserved. Specifications are subject to modification, revision and improvement.
