Therapies
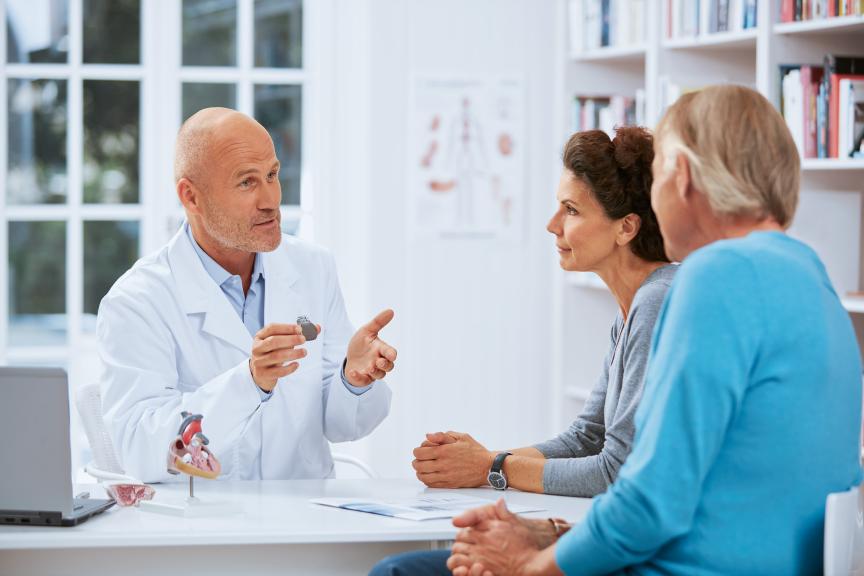
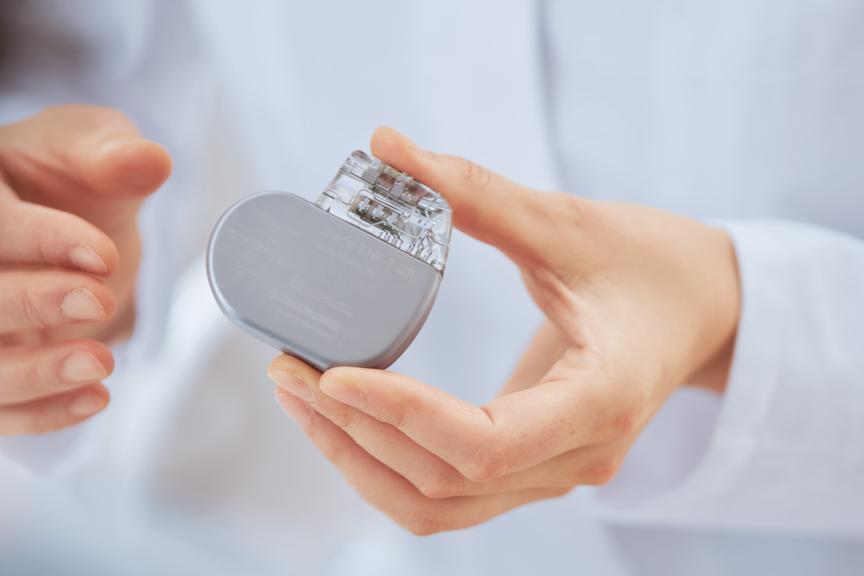
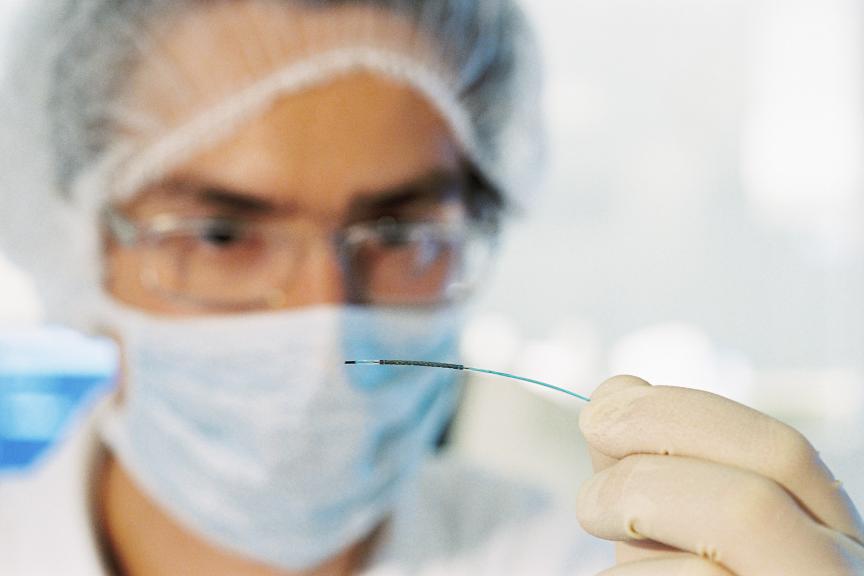
At BIOTRONIK, we are committed to helping people with heart and blood vessel diseases to lead healthy and fulfilling lives. But how do pacemakers, defibrillators or stents actually work? In this section, we introduce the main therapy options that can help with cardiovascular health conditions. Please head to our product catalog if you require more in-depth information about a certain product.
Image