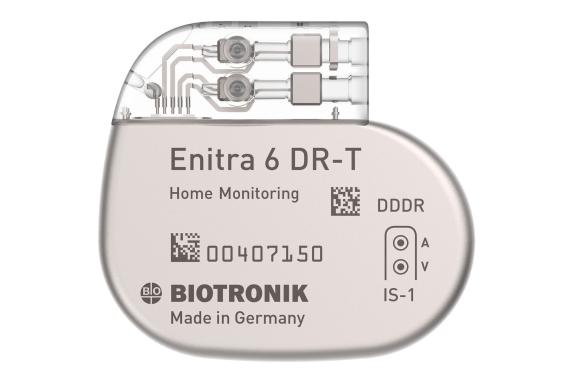
Solvia Rise DR-T/SR-T
Solvia Rise daje możliwość wyboru. Skorzystaj z szerokiej gamy opcji leczenia, takich jak fizjologiczna stymulacja, która umożliwia niemal samoistną regulację pojemności minutowej serca za pomocą technologii Closed Loop Stimulation (CLS).
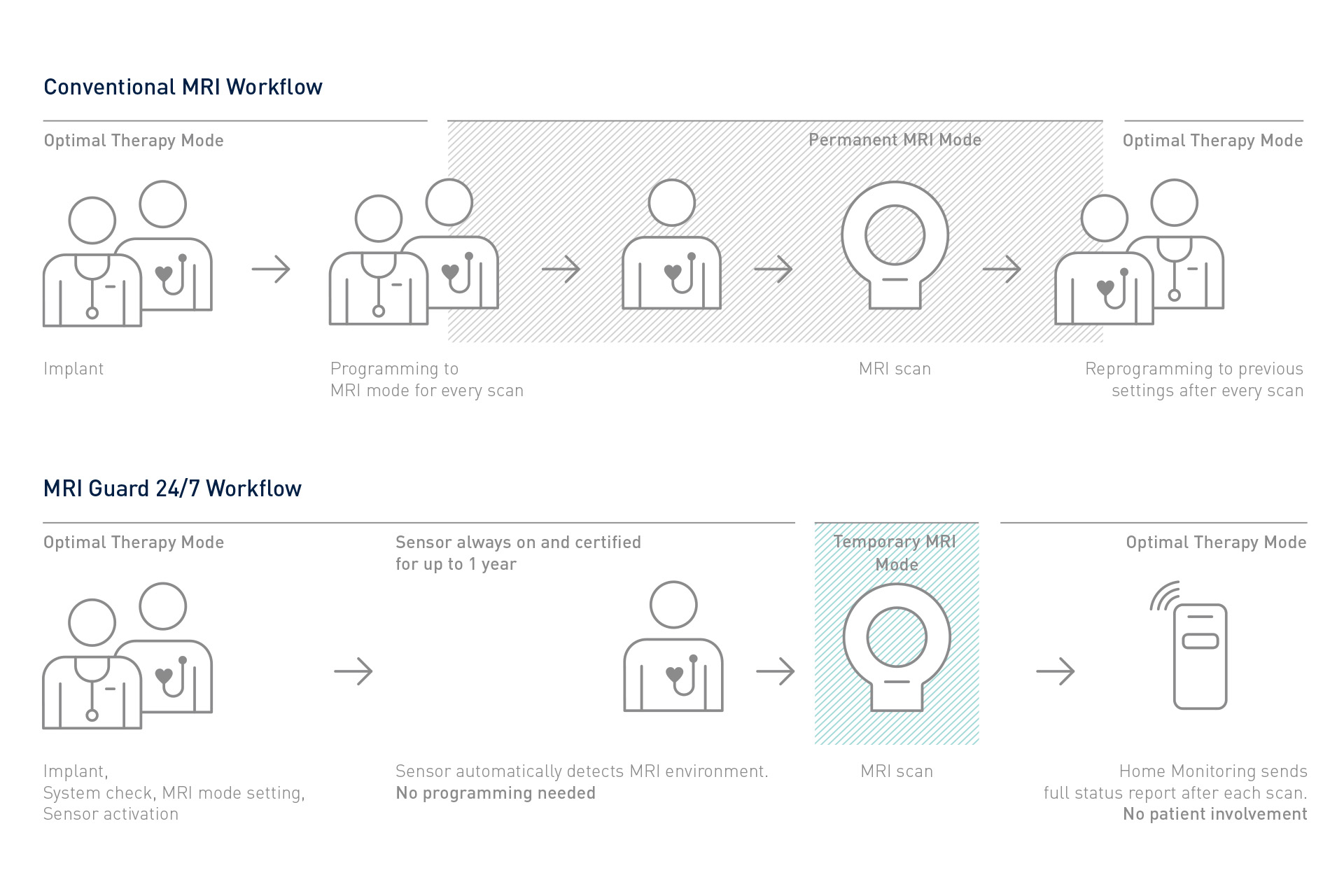
Jednocześnie stymulator Solvia Rise pozwala na automatyzację wielu rutynowych zadań podczas zabiegu wszczepienia, ambulatoryjnych badań kontrolnych, zdalnego monitorowania i skanowania z wykorzystaniem tomografii rezonansu magnetycznego (MRI). Zapewnia pacjentom unikalną fizjologiczną stymulację serca, usprawnienie terapii i oszczędność czasu w codziennej pracy – aby więcej pacjentów mogło skorzystać z bardziej spersonalizowanej opieki.
Najważniejsze cechy produktu
Działanie w zgodzie z fizjologicznymi potrzebami pacjentów dzięki funkcji Closed-Loop-Stimulation
Instrukcja obsługi
Literatura
1) Instrukcja obsługi BIOTRONIK Amvia Edge, instrukcja obsługi Medtronic Azure XT DR MRI SureScan™; instrukcja obsługi Boston Scientific Accolade MRI™; instrukcja obsługi Abbott Assurity MRI™; instrukcja obsługi urządzenia MicroPort Alizea™. 2) Lindovska M, Kameník L, Pollock B, et al. Clinical observations with Closed Loop Stimulation pacemakers in a large patient cohort: the CYLOS routine documentation registry (RECORD). Europace. 2012; 14: 1587-1595. 3) Santini M, Ricci R, Pignalberi C, et al. Effect of autonomic stressors on rate control in pacemakers using ventricular impedance signal. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2004; 27: 24-32. 4) Mabo P, Victor F, Bazin P, et al. A randomized trial of long-term remote monitoring of pacemaker recipients (the COMPAS trial). Eur Heart J. 2012; 33(9): 1105-1111. 5) Sharma PS, Patel NR, Ravi V, et al. Clinical outcomes of left bundle branch area pacing compared to right ventricular pacing: Results from the Geisinger-Rush Conduction System Pacing Registry. Heart Rhythm. 2022; 19(1): 3-11. 6) De Pooter J, Ozpak E, Calle S, et al. Initial experience of left bundle branch area pacing using stylet-driven pacing leads: A multicenter study. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2022; 33(7): 1540-1549. Wyłączenie odpowiedzialności: Ten materiał podsumowuje jedynie badawcze użycie narzędzi do stymulacji układu przewodzącego (CSP) zastosowane przez De Pooter i in. w badaniu klinicznym. Proszę pamiętać, że elektroda Solia S nie posiada zatwierdzenia do stosowania w CSP. Narzędzia do CSP firmy BIOTRONIK nie posiadają obecnie zatwierdzenia dla stosowania do stymulacji układu przewodzącego w Stanach Zjednoczonych. Zawartość niniejszego komunikatu nie jest przeznaczona dla lekarzy w Stanach Zjednoczonych. 7) Menezes AS, Daher MT, Nascente CM, Moreira HG, Moreira TAC, Campos RN. Correlation among Closed Loop Stimulation, cardiopulmonary capacity, and quality of life PBMR. 2003; 8(2): 119-124. 8) Pavri BB, Russel S. An impedance sensor is superior to an accelerometer for chronotropically incompetent patients with sinus node dysfunction: results of a pilot study with a dual sensor pacemaker. Circulation. 2006; 114: II_749. 9) Coenen M, Malinowski K, Spitzer W, et al. Closed Loop Stimulation and accelerometer based rate adaptation: results of the PROVIDE study, Europace. 2008; 10: 327-333. 10) Malinowski K. Interindividual comparison of different sensor principles for rate adaptive pacing PACE. 1998; 21(PT II): 2209-2213. 11) Abi-Samra FM, Singh N, Rosin BL, DwyerJV, Miller C. Europace. 2013; 15: 849-856. 12) Puglisi A, Favale S, Scipione P, et al. Overdrive versus conventional closed-loop rate modulation pacing in the prevention of atrial tachyarrhythmias in brady-tachy syndrome: on behalf of the Burden II study group. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2008; 11: 1443-55. 13) Ikeda S, Nogami A, Inoue K, et al. Closed‐loop stimulation as a physiological rate‐modulated pacing approach based on intracardiac impedance to lower the atrial tachyarrhythmia burden in patients with sinus node dysfunction and atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2020; 31: 1187-1194. 14) Coenen M, Malinowski K, Spitz W, et al. Closed loop stimulation and accelerometer-based rate adaptation: results of the PROVIDE study. Europace. 2008; 10: 327-333. 15) Nattel S, Burstein B, Dobrev D. Atrial remodeling and atrial fibrillation: mechanisms and implications. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2008; 1(1): 62-73. 16) Dane w pliku 17) Varma N, Epstein AE, Irimpen A, et al. Efficacy and safety of automatic remote monitoring for implantable cardioverter-defibrillator follow-up: the Lumos-T Safely Reduces Routine Office Device Follow-up (TRUST) trial. Circulation. 2010; 122(4): 325–332. 18) Mullane S, Michaelis K, Henrickson C, et al. Utilization and programming of an automatic MRI recognition feature for cardiac rhythm management devices. Heart Rhythm O2. 2021; 2: 132-137. 19). Dane w pliku. 20) Siddamsetti S, Shinn A, Gautam S. Remote programming of cardiac implantable electronic devices: a novel approach to program cardiac devices for magnetic resonance imaging. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2022;33(5):1005–1009. 21) Watanabe E, Yamazaki F, Goto T, et al. Remote management of pacemaker patients with biennial in-clinic evaluation: continuous Home Monitoring in the Japanese At-Home study: A randomized clinical trial. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. maj 2020;13(5):e007734. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.119.007734. 22) Garcia-Fernández FJ, Asensi JO, Romero R, et al. Safety and efficiency of a common and simplified protocol for pacemaker and defibrillator surveillance based on remote monitoring only: a long-term randomized trial (RM-ALONE). Eur Heart J. 2019; 40(23): 1837-1846. 23) Ricci RP, Morichelli L, Quarta L, et al. Long-term patient acceptance of and satisfaction with implanted device remote monitoring, Europace. 2010; 12(5): 674-679. 24) Dane w pliku 25) Dane w pliku 26) Amvia Edge SR-T 10 lat; Ograniczona gwarancja elektronicznych kardiologicznych wyrobów do implantacji BIOTRONIK; Streszczenie ograniczonej gwarancji Medtronic; Informacje i formaty ograniczonej gwarancji Boston Scientific; Abbott CRM Instrukcja referencyjna procedur gwarancyjnych; Instrukcja implantów MicroPort Alizea DR™/Alizea SR™. 27) Amvia Edge DR-T 8 lat; Ograniczona gwarancja elektronicznych kardiologicznych wyrobów do implantacji BIOTRONIK; Streszczenie ograniczonej gwarancji Medtronic; Informacje i formaty ograniczonej gwarancji Boston Scientific; Abbott CRM Instrukcja referencyjna procedur gwarancyjnych; Instrukcja implantów MicroPort Alizea DR™/Alizea SR™. 28) Amvia Edge SR-T: przy 2,5 V/0,4 ms, 60 bpm, 500 Ω; stymulacja: 50%, Home Monitoring: WYŁ, QuickCheck: WYŁ, telemetria bezprzewodowa: WYŁ. 29) Amvia Edge DR-T: A: 2,5 V/0,4 ms, 60 bpm, 500 Ω, stymulacja: 50%, RV: 2,5 V/0,4 ms, 60 bpm, 500 Ω, stymulacja: 5%, Home Monitoring WYŁ, QuickCheck: WYŁ, telemetria bezprzewodowa: WYŁ, hamowanie stymulacji komorowej WŁ.